
Introduction
In order to fully understand how on-page optimisation can improve your website’s global performance, you need to begin by understanding how the search results work and how search engines and on-page optimisation have changed over time.
Over the years, search engines evolved from simple keyword matching and keyword density measuring, to a more sophisticated understanding of the context and user intent behind keywords. This had an impact on the importance of content in SEO, with John Mueller hinting that as Google gets better at understanding content, links may become less important. With each algorithm update, Google keeps reminding us how important it is to create content for real people, and not for search engines.
All this had an impact on content optimisation practices, which evolved from the simple use of keywords and keyword density-focused content creation, to a focus on the quality, relevance and value of a piece of content.
So, nowadays, how should you approach on-page optimisation? The answer is simpler than you may think. In order to succeed at on-page optimisation, you must follow these three principles:
- Understand user intent and the context of the search terms.
- Get familiar with entities.
- Adopt a people-first content creation approach.
Let’s delve into each of these concepts in more detail.
1. Understand user intent and the context of the search terms
Google uses context and user intent to identify the relevancy of a page for a certain search term, as well as the relevance of the content for the user’s needs. Over the years, Google has been working on improving how its systems understand these concepts, and this is why context and user intent are more important than ever. There is absolutely no content optimisation project that you should start without first understanding what the user intent is and what the context is for the search terms that you want to optimise your content for.
There were two important Google algorithm milestones here: Hummingbird and RankBrain. These two updates to Google’s systems were responsible for how well Google understands queries and content:
- Hummingbird was the beginning of semantic search. This was when the concept of entities was introduced to search. This update to Google’s search algorithm enabled it to move from exact keyword matching, to understanding the context of the words and the relationships between them. Hummingbird was the first step that helped Google get better at understanding how relevant a page is for a search term.
- RankBrain was the introduction of AI and machine learning to Google’s search systems. Self-trained to answer new and unique search queries based on previously acquired knowledge, this model enabled Google to learn from user behaviour and user satisfaction, as well as the location of the user, the device they are using to perform the search, and the user intent.
Hummingbird and RankBrain helped Google to understand the relevance of content to search terms, the relationships between different search terms, as well as helping to improve the search results overall by understanding how users search and the intent behind the searches they perform.
It is important to understand that user intent is not static. It can change and fluctuate, depending on location, language, device, and it can also change over time. Also, sometimes, search results can be quite mixed. This can be related to a high degree of ambiguity of a search term, or just the fact that the user intent is not defined well enough at that moment. This is why it is extremely important, before the start of any optimisation project, to always look at the search results and to select the right keywords – i.e. keywords that are not too ambiguous.
Be aware that user intent is very difficult to analyse at scale. Imagine that you have to analyse user intent for 200 keywords. Of course, you can use tools like Semrush and these tools are getting better at defining user intent, but I would recommend that for really important, priority search terms, you look at the search results, because then you will have more clarity on what the context is and what the user intent is that you want to optimise your content for.
If you have already created content and you notice that you have suddenly completely lost traffic for a keyword, this can be an indicator that the user intent has changed. In this case, you should look in more detail at this keyword.
How can you put all this into practice?
Before starting your content optimisation project, it is really important to look at the SERP to identify which elements are there. This will help you define the context and the user intent behind the search term you are optimising for. Are there knowledge panels? Are there ads? Are there top stories? Are there “people also ask” boxes? Are there featured snippets? What kind of content is on the SERP? What kind of layout does the SERP have? If you are targeting multiple markets, make sure that you carry out this analysis for all the markets you are targeting. Users search differently in different countries, and this, naturally, impacts the search results.
You should also look at the search results themselves. What kind of pages are the top-performing URLs? Are there blog posts and guides? If so, you can infer an informational user intent. Or, if there are shopping pages, such as catalogues or product pages, you can infer a transactional user intent.
Analysing all these elements will help you identify the user intent. Then, you will have a solid basis for your content creation project, because you will have selected the right keywords and you will know what the context is behind those keywords.
2. Get familiar with entities
Next, it is important to understand the concepts of entities and natural language processing models.
Entities were introduced to Google search with the Hummingbird update and the start of semantic search. Google defines entities as “a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable”. An entity can be an idea, object, colour, person or place. By understanding different concepts, Google is also better at understanding how these concepts are related to one another, which enables it to surface better search results for users.
Google created its entity knowledge base from authoritative sources on the internet, such as Wikipedia. This entity knowledge base is further used to train Google’s natural language processing models. The natural language processing models are trained to extract, process and identify entities and the relationships between them, which allows Google to better define concepts and understand the relationships between them, enabling it to get better at matching relevant content to a query.
When it comes to natural language processing models, it is important to know about BERT and MUM:

Based on these two natural language processing models, Google shapes the search results. With BERT and MUM, Google got better at understanding the relationships between words and how words fit in a text, which enables it to better understand the structure and meaning of the text:
- BERT was the first big improvement in Google search after RankBrain, which enabled Google’s systems to understand how words fit together in a text. This advancement improved how Google defined the meaning of ambiguous words.
- MUM is more powerful technology than BERT. With this technology, Google became better at understanding more complex queries, whilst also going beyond understanding of just text. Nowadays, Google’s systems can understand images, videos and audio content too. MUM also removed the barriers when it comes to international search, as it is trained on 75 languages, which improved international search overall.
All these improvements highlight how important it is to create meaningful content which will be useful for users, whilst also using different content formats to ensure a good user experience.
How can you put all this into practice?
When it comes to identifying entities, I would suggest using Google’s natural language processing tool. This tool has a demo which is open source and anyone can use it. This tool is trained on Google’s models, which is really insightful.
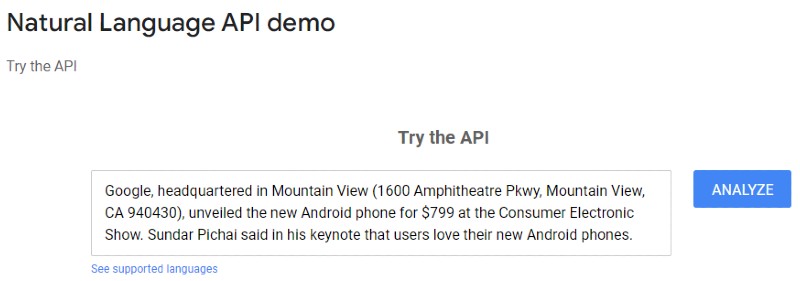
What you have to do when using this tool is go to the search results, go to the page that you want to analyse, then copy the content and paste it into the tool. Then, you just have to run the tool and Google will list all the important concepts and topics (i.e. entities) that it has identified in this content (see an example below). These entities are listed by the tool with their salience score. Salience defines how important an entity is for the whole text. The salience score goes from 0 to 1.
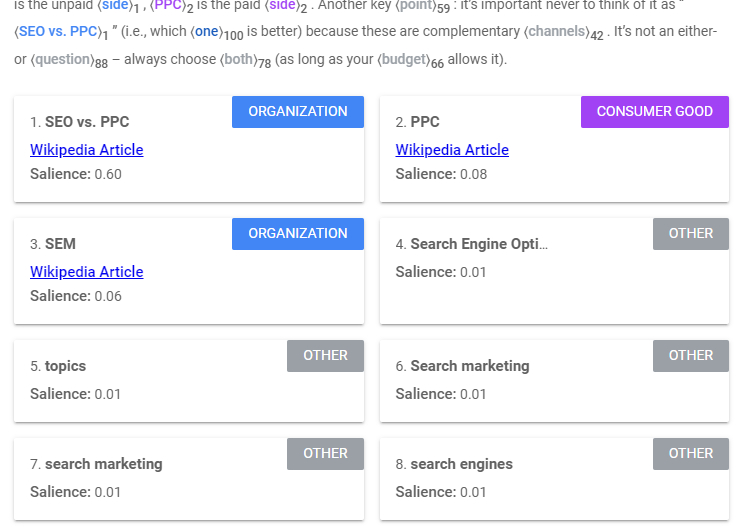
Just to review the steps when it comes to content optimisation: start with defining the user intent and context behind the target search term, identify all the entities related to your topic, check how the top-performing pages are structured, and then use all this information as your framework to write your content or create copywriter guidelines.
Click here to read our case study if you want to learn how we improved a client’s organic rankings on Google using entity-based optimisation.
3. Adopt a people-first content creation approach
This takes us to the final point, which is to adopt a people-first content creation approach. Here, you need to get familiar with E-E-A-T and helpful content updates.
Google originally created a framework called E-A-T in order to assess and ensure the quality of the content on the web. This framework is used by human quality raters who, following the guidelines, assess the quality of the pages in the search results. Not that long ago, Google added another E to E-A-T, so that it now stands for expertise, experience, authority and trust.
The raters assess expertise, experience, authority and trust independently, using a different set of criteria for each.
This framework helps Google ensure that users are served quality and relevant content from trustworthy sources, and thus has a great impact on the search results. To help webmasters understand and apply the E-E-A-T framework to their content, Google created Search Quality Rater Guidelines.
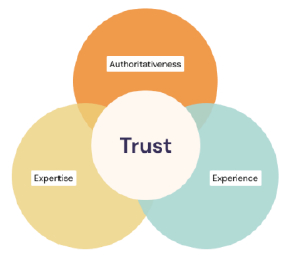
It is important to have the E-E-A-T framework in mind when creating your content, so that you build and represent yourself as an expert with authority and experience in your field, ensuring that the users (and Google) trust you.
- Experience: You should show that you have first-hand experience on the topic, for example through the use of case studies, videos and content.
- Expertise: You should show that you have the necessary knowledge on a topic by covering all different aspects of the main topic you are targeting.
- Authority: You should show through your content and your website that you are a reliable source for the topic that you are dedicating your website to.
When users are familiar with who you are, what others think about you, and are able to learn from your content and get the answers they are looking for, you will be considered as an authority and trustworthy source of information.
Another important concept to understand is helpful content updates, which were introduced in 2022. These were updates to Google’s systems which were focused on rewarding and surfacing content which is valuable and created for real people, not search engines. These updates are part of Google’s continuous effort to surface better search results, and to reduce the amount of low-quality and spammy content which has little to no value. To guide webmasters and content creators in creating content for real people, Google published advice on helpful content creation. This guide contains questions webmasters should go through to evaluate whether their content is helpful and made for real people.
How can you put all this into practice?
When it comes to E-E-A-T guidelines, you need to showcase your experience and expertise. You can do this through your content by covering multiple stages of the user information funnel – i.e. informational, commercial, transactional. Ensure you answer important questions users might have about your topic. Try to offer the most valuable and high-quality content to your users using multiple formats (e.g. text, images, videos) to enrich the experience of your users.
You also have to show you are an authoritative source on your topic. You can do this throughout your whole website, but it is particularly good to have a really informative “about us” page. Also, if you have a blog with multiple people contributing, it is good to show who these people are and if they are experts on a certain topic. You can also show what others think about you by including testimonials and product reviews. This is a transparent way in which you can build trust with your users.
When it comes to creating content for people, you should create useful content for your intended audience, demonstrating that you have first-hand expertise and knowledge on the topic. The primary focus and purpose of your website should be really clear to everyone, and of course you need to make sure that you are following Google’s guidelines.
Successful case studies
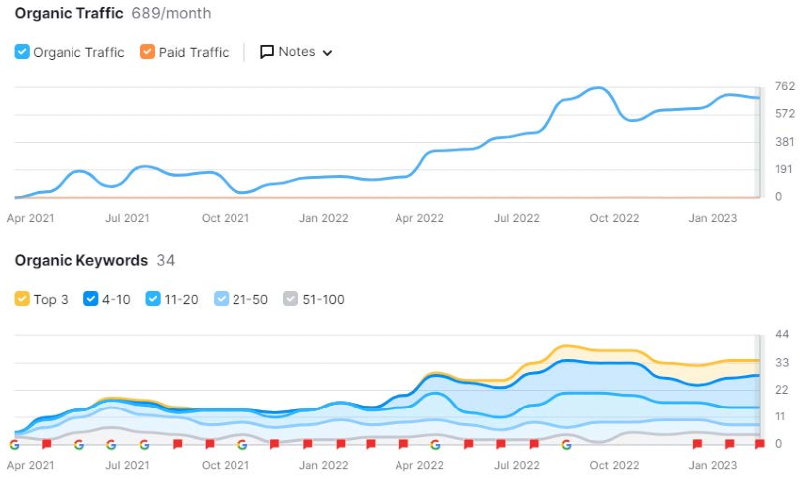
At Webcertain, we have worked on multiple content optimisation projects, relying on the principles outlined in this blog post. Below are a few examples of how this approach has led to some very positive results for our clients, with traffic increasing substantially after the content optimisation.
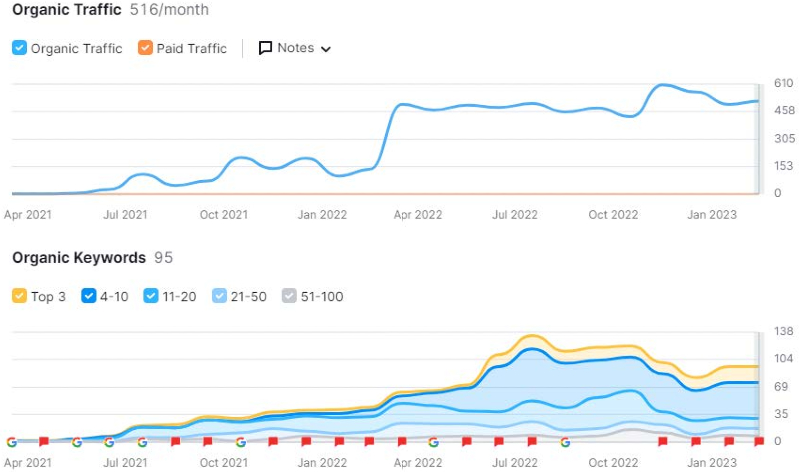
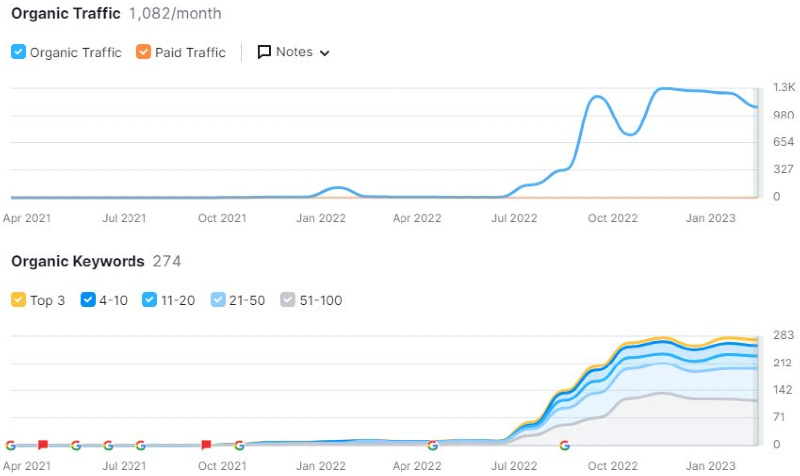
Key takeaways
To summarise, remember the following when optimising your content:
- Content is more important than ever.
- Dedicate time and resources to creating valuable and high-quality content.
- Follow Google’s guidelines, especially if you are working in a sensitive industry like health or finance.
- Investigate user intent and context before starting any optimisation project.
- Write for real people, not search engines.
Want to watch the full webinar recording?
If you want to learn more about how on-page optimisation can improve global performance, watch our webinar recording on this topic here! The webinar goes into more depth than this blog post and covers:
- The results international brands have achieved through on-page optimisation
- Why this approach is so important in 2023
- How to get started with an optimisation project
- Top tips for driving results and boosting global rankings








